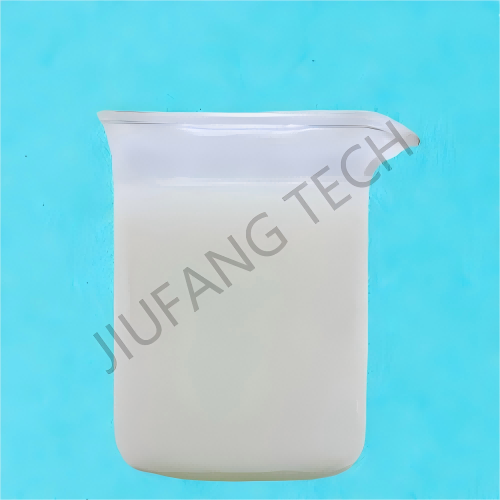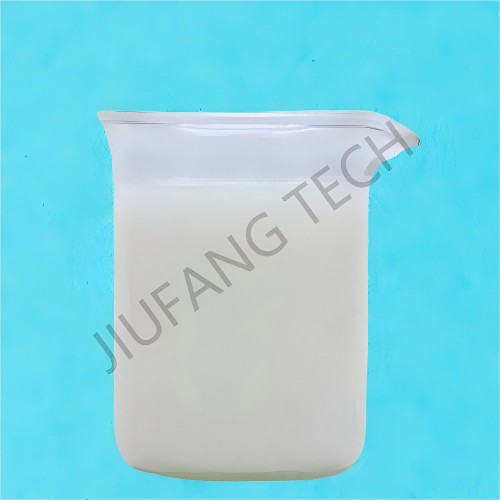
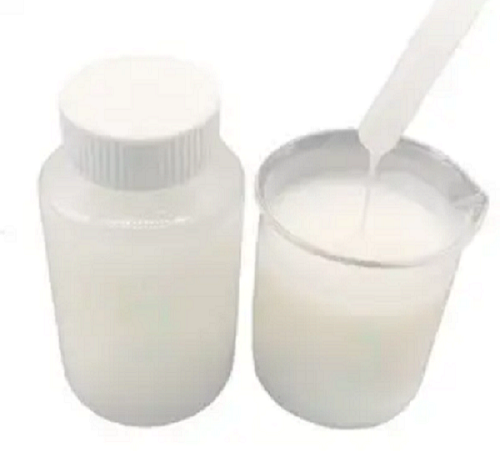
Cationic PAM Emulsion
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 2000Metric Tons per Month
1.Output:Produce 2000tons per month cationic emulsion flocculant.
2.Emulsion flocculant cationic is used for dewatering in refinery or STP.
3.The advantage of cationic emulsion flocculant are easily soluble in water.
Download
The flocculation mechanism of water-in-oil (W/O) polyacrylamide emulsion (cationic emulsion flocculant)is a comprehensive process in which it functions as a emulsion flocculant cationic in an aqueous system. It not only includes the flocculation characteristics of the molecule emulsion flocculant PAM itself, but also involves the special process of emulsion demulsification to release the active ingredients.
The specific process can be divided into the following key steps:
1. Emulsion Demulsification and PAM emulsion cationic release
The system structure of water in oil PAM emulsion is as follows:
The water phase (containing the molecules of emulsion flocculant cationic or their dispersions) serves as the dispersed phase, is wrapped by the continuous oil phase (such as mineral oil, vegetable oil), and is stabilized by emulsifiers (such as Span type, Tween type) to form an emulsion. When this emulsion is added to the water system to be treated (such as sewage, suspension), due to the osmotic pressure difference between the external environment (water phase) and the internal water phase of the emulsion, as well as the dissolution/dispersion of the emulsifier in the water phase, the stability of the emulsion is disrupted, and demulsification occurs: The oil phase is dispersed into tiny oil droplets in the large amount of water phase and gradually separates from the water phase.
The PAM emulsion cationic encapsulated inside (usually a water soluble polymer or a dispersion that can dissolve rapidly in the water phase) is released into the water system, forming a PAM emulsion cationic molecular solution or dispersion.
2. Adsorption of molecules of emulsion flocculant PAM on Colloidal Particles
The released molecules of emulsion flocculant PAM interact with the colloidal particles (such as sediment, organic matter, microorganisms, etc.) in the water through polar groups (such as the amide group -CO - NH₂), achieving adsorption: Hydrogen bond interaction:
The amide group in the molecule emulsion flocculant PAM forms hydrogen bonds with polar groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) on the surface of the colloidal particles.
Van der Waals force: The long chain structure of the polymer chain generates Van der Waals attractive forces with the particle surface.
Electrostatic adsorption: If the colloidal particles are negatively charged (most natural colloids such as clay, bacteria, etc.), if the molecular chain of emulsion flocculant PAM contains a small number of cationic groups (such as cationic PAM), it can be adsorbed onto the particle surface through electrostatic attraction. Even for non ionic or anionic PAM, selective adsorption can occur with the particle surface through local charge density differences in the chain segments.
3. Electro neutralization
Effect Colloidal particles usually carry charges (mostly negative) due to the adsorption of ions or groups on their surfaces. It is difficult for the particles to aggregate due to "like charge repulsion".
The molecules of emulsion flocculant PAM (especially cationic or amphoteric types) can neutralize some of the surface charges by adsorbing onto the particle surface, reducing the electrostatic repulsive force between the particles and making the particles more likely to approach and aggregate.
4. Bridging Flocculation (Core Mechanism) The long chain polymer(emulsion flocculant PAM) structure of PAM is the key to its high efficiency flocculation: A single the molecular chain of cationic emulsion flocculant can simultaneously adsorb multiple colloidal particles (each particle surface adsorbs different segments of one or more molecular chains). Through the "molecular chain bridge", the dispersed small particles are connected to form larger flocs ("bridging structure"). As the floc size increases, gravity dominates their sedimentation, or they are separated by filtration, flotation, etc.
The flocculation mechanism of water in oil PAM emulsion cationic can be summarized as: Emulsion demulsification releases PAM molecules → PAM binds to colloidal particles through adsorption → Electro - neutralization reduces particle repulsion → Long - chain molecules bridge and connect particles to form large flocs → Solid - liquid separation is achieved.
Its advantage is that the emulsion form allows PAM (emulsion flocculant cationic)to disperse and release quickly, avoiding the problem of incomplete dissolution of solid PAM, thus improving the flocculation efficiency.
The main application fields of emulsion flocculant cationic are:
1. Sewage treatment Emulsion flocculant PAM can be used in the treatment of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater. Through the flocculation effect, pollutants such as suspended solids, organic matter, and heavy metal ions in the water are removed to improve water quality.Cationic emulsion flocculant has a significant treatment effect on wastewater from industries such as printing and dyeing,papermaking and food processing.
2. Sludge dewatering PAM emulsion cationic polyacrylamide can effectively separate the water from the solid particles in the sludge, reduce the moisture content of the sludge, and facilitate subsequent treatment and disposal.
3. Mining field In the mineral processing process, emulsion flocculant PAM can be used for ore flotation, tailings treatment, etc. to improve the recovery rate of minerals and reduce wastewater discharge.
4. Papermaking industry It is used for paper strengthening, retention and drainage aid, etc., to improve the quality and production efficiency of paper.
5. Petroleum industry Emulsion flocculant can be used for oilfield wastewater treatment, drilling mud treatment, etc.to improve the efficiency and environmental protection of oil extraction.

Industry-specific attributes
| Name | Emulsion flocculant cationic | |||
| Chemical Formula | (C3H5NO)n | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003/5/8 | |||
Other Attributes
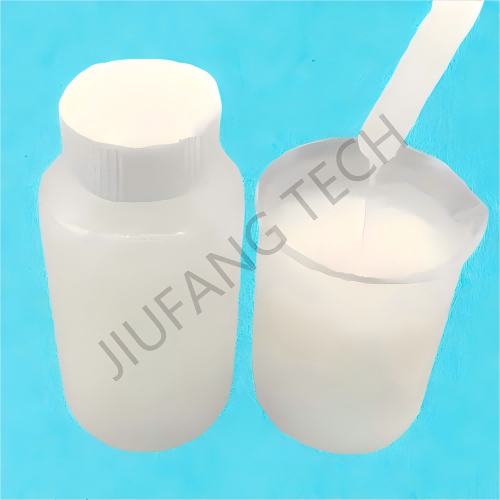
| Appearance | Milky,White Viscous Emulsion | |||
| Solid Content | 45% | |||
| Molecular Weight10*6 | 15~30 | |||
| Specific Granvity(25℃) | 1.0 | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| PH Value | 6.5~7.5 | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | <30 | |||
| Cationic charge(%) | 80 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















