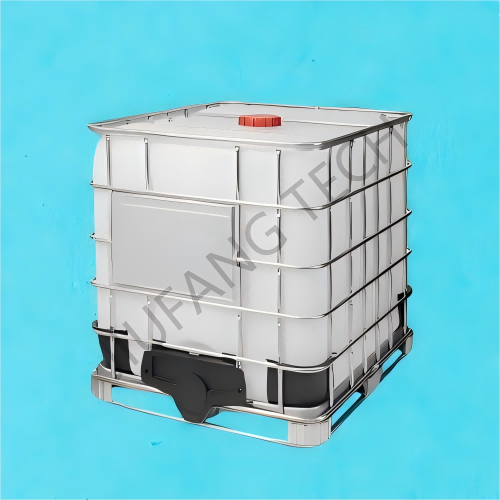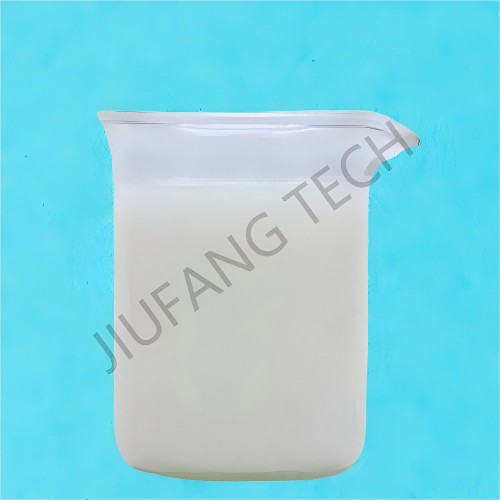
Anionic Polyacrylamide Emulsion For Sewage treatment
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 2000Metric Tons per Month
Anionic polyacrylamide wastewater treatment is a key link in the pretreatment process for removing the SS value. Selecting the suitable anionic emulsion for sewage treatment will achieve a good performance in the primary step and reduce the load of the next processes.
Download
Selecting an appropriate anionic emulsion for sewage treatment polyacrylamide (APAM) for a specific application scenario requires matching based on the core requirements of the scenario, environmental conditions, and key product parameters.
The core logic is "demand orientation + parameter adaptation + experimental verification". The following are the specific selection methods:
1. Define the Core Requirements of the Application
Water Treatment (Flocculation/Sedimentation): The core requirement is "rapid settlement of suspended solids", with attention paid to the size of flocs, sedimentation speed, and the clarity of the supernatant.
Sludge Dewatering using anionic for sewage dewatering: The core requirement is reduction of sludge moisture content, focusing on the filter cake peelability, filter cloth permeability, and dewatering efficiency.
Oil Exploitation (Enhanced Oil Recovery/Drilling): The core requirements are "thickening/stability", with emphasis on solution viscosity, salt resistance, and shear resistance.
Papermaking (Retention/Strengthening): The core requirement is "fiber retention rate", paying attention to the adsorption capacity with fillers and the improvement effect on paper strength.
2. Match Key Parameters of anionic polyacrylamide wastewater agent with Scenario Characteristics The core parameters of anionic emulsion for sewage treatment (molecular weight, anionic degree, solid content, etc.) need to be precisely matched with the characteristics of the scenario.
3. Adjust the Selection Based on Environmental Conditions Environmental factors in the scenario can significantly affect the performance of anionic for sewage dewatering, and targeted adjustments are required.
4.Verify the Optimal Model through Experiments
After theoretical selection, jar test of anionic polyacrylamide wastewater agents are needed for verification.
5. Balance Economy and Operability
Avoid the mindset of "the higher the parameters, the better": For example, products with a high anionic degree are more expensive, but in scenarios with low charge substances, their performance may not be better than that of products with a medium anionic degree, and instead, they increase costs.
Operational Adaptability: For continuous production lines, emulsion polyacrylamide for sewage treatment APAM that is easy to measure and dissolve quickly should be selected (to avoid dust from powder). For batch - type treatment, there is more flexibility in selection, but attention should be paid to the storage stability of the emulsion (sealed, protected from light, with a shelf - life of usually 6 months).
Summary:
1. Define the core requirements of the scenario (flocculation/dewatering/thickening, etc.);
2. Initially screen the molecular weight and anionic degree based on water quality characteristics (turbidity, pH, salinity);
3. Adjust the model in combination with environmental conditions (temperature, shear force);
4. Verify the effect through jar test of anionic for sewage dewatering and compare costs;
5. Finally determine the optimal model. For example, when treating high turbidity and high Fe³⁺ wastewater from a steel plant, selecting sulfonic group anionic emulsion for sewage treatment APAM with a high molecular weight (20 million) and a medium high anionic degree (30% - 40%) can quickly form large flocs, increasing the sedimentation efficiency by more than 40%.

Industry-specific attributes:
| Name | Emulsion polyacrylamide for sewage treatment | |||
| Application | Anionic for sewage dewatering | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
Other Attributes:
| Appearance | Milky,White Viscous Emulsion | |||
| Activate Content | 40% | |||
| Molecular Weight10*6 | 12~16 | |||
| Specific Granvity(25℃) | 1.0 | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| PH Value | 6.5~7.5 | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | <30 | |||
| Anionic charge | 30% | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability:
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time:
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















