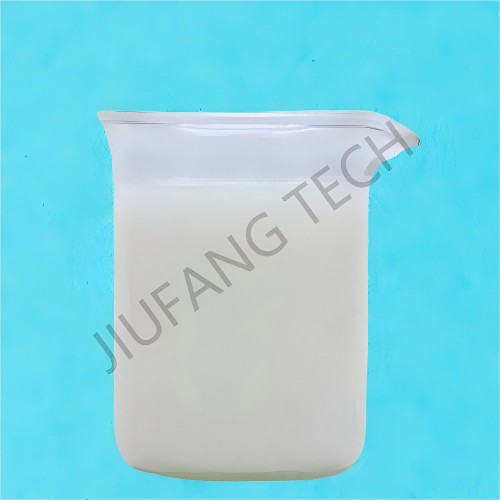
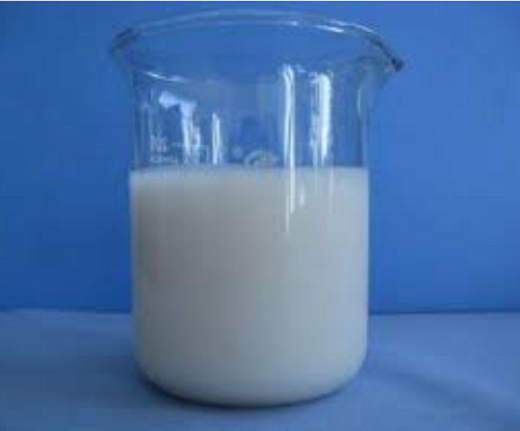
Cationic Polyacrylamide Emulsion For Sludge treatment
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 2000Metric Tons per Month
1.Polyacrylamide sludge dewatering as a type of coagulant which is made by acrylamide with DAC or DMC after copolymerization.
2. Cationic liquid flocculant, also named polyacrylamide emulsion for sludge dewatering, normally means use emulsion for sludge dewatering.
Download
Improving the dewatering efficiency of cationic polyacrylamide polymer (cationic liquid flocculant) requires comprehensive regulation of multiple aspects, including reagent selection, process condition optimization, pretreatment synergy, and equipment matching.
Targeted improvements should be made in combination with the characteristics of oily sludge (such as oil content, particle charge, moisture content, etc.).
The specific measures of polyacrylamide emulsion for sludge dewatering are as follows:
Precise Selection of cationic liquid flocculant: Matching Sludge Characteristics The matching degree between the performance of cationic polyacrylamide polymer (cationic degree, molecular weight, molecular structure) and the properties of sludge is the core determinant of dewatering efficiency. It is necessary to make "customized" selections according to the characteristics of the sludge. The dewatering rate can be improved by optimizing the cationic degree and matching the molecular weight.
Different dewatering equipment has different requirements for floc strength. Plate and frame filter presses and box type filter presses require cationic polyacrylamide polymer with medium high molecular weight (8-12 million). The long molecular chains of cationic polyacrylamide polymer can form tough flocs that can withstand high pressure filtration. Horizontal spiral centrifuges and belt filter presses require polyacrylamide sludge dewatering with medium low molecular weight (5-8 million) to avoid problems such as blockage during centrifugation due to overly large flocs or poor water permeability during filtration.
At the same time, the dewatering rate can be increased by precisely controlling the dosage, improving the dosing method, and controlling the stirring intensity and time. Pretreatment for demulsification and oil removal is also a way to improve the dewatering rate. If the sludge contains a large amount of emulsified oil (oil content > 10%), inorganic demulsifiers (such as PAC, FeCl₃, Al₂(SO₄)₃) or surfactants (such as dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride) can be added to break the double electric layer of oil droplets, causing the oil droplets to coalesce and float or combine with solids, reducing the obstruction of the oil film to polyacrylamide sludge dewatering. After demulsification, free oil can be removed through air flotation or centrifugation, reducing the oil content of the sludge to less than 5%. Then, when adding polyacrylamide sludge dewatering, the reagent consumption can be reduced by more than 30%. Other auxiliary measures mainly include sludge homogenization, controlling storage conditions, on line monitoring, and dynamic adjustment.

Industry-specific attributes
| Name | Cationic liquid flocculant | |||
| Application | Polyacrylamide emulsion for sludge dewatering | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
Other Attributes
| Appearance | White emulsion polyacrylamide | |||
| Content | 48% | |||
| Viscosity Range(ml/g) | 1200~1600 | |||
| Residue | 0.12% | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| Cationic Charge | 80% | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | 40 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















