CPAM
Brand JF
Product origin China
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 10000MT/Year
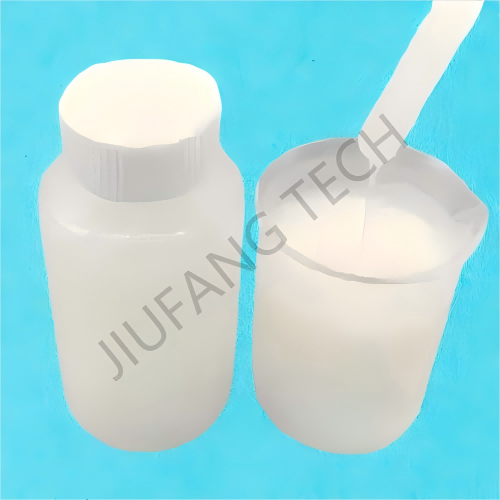
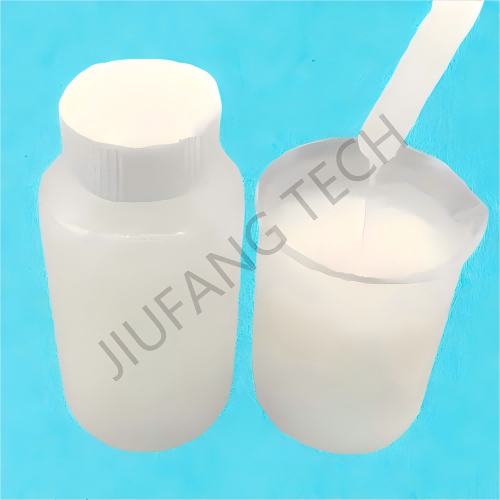
1. Emulsion flocculant for water is a white emulsion of CPAM flocculant which is easily soluble in water.
2. Flocculant emulsion CPAM is a cross linked polyacrylamide and has a good performance in water filtration.
3. Flocculant emulsion CPAM has a good performance in treating high content water of sludge.
Download
Cationic Polyacrylamide Emulsion (CPAM flocculant--JF1115) is the liquid form of flocculant CPAM.
It is prepared through the inverse emulsion polymerization process. The molecular chain of flocculant emulsion CPAM contains positively charged groups (such as quaternary ammonium salts).
CPAM flocculant combines the charge-neutralizing ability of cationic PAM with the unique advantages of the flocculant emulsion CPAM dosage form.
The product characteristics of flocculant emulsion CPAM are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1.Morphology and Basic Characteristics
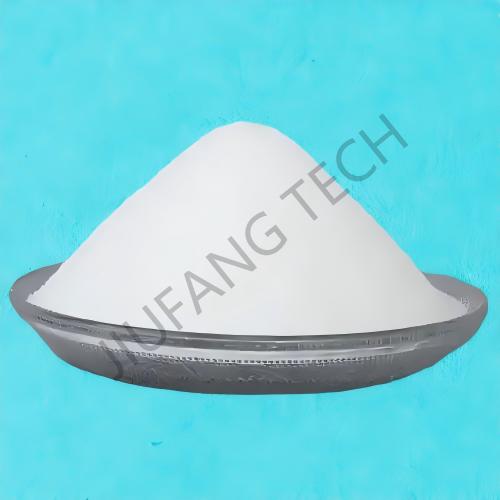
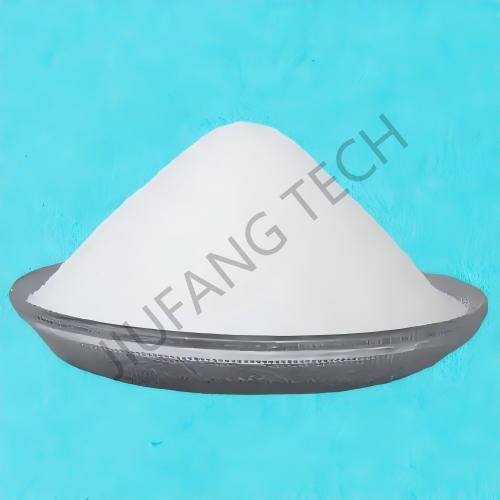
Physical Form of CPAM flocculant : Flocculant emulsion CPAM appears as an oil-in-water or water-in-oil emulsion (mostly milky white or light yellow viscous liquid in appearance). The solid content of emulsion CPAM flocculant is usually between 20%-50% (JF1115 solid content is 48%).
Molecular Characteristics of flocculant CPAM: The degree of cationicity can be precisely adjusted (10%-80%), with a wide molecular weight range (from tens of thousands to several million). The molecular chains of flocculant CPAM are more evenly dispersed in the emulsion. The molecular structure is cross linked polyacrylamide, which is a type of emulsion flocculant for water treatment.
2. Core Product Advantages of flocculant emulsion CPAM
A. Extremely Fast Dissolution Speed
Powdered PAM requires 40-60 minutes of stirring for dissolution and is prone to agglomeration. In contrast, the flocculant CPAM emulsion-type(JF1115) can dissolve rapidly within 5-15 minutes without the need for long-term stirring. This can significantly shorten the operation process, especially suitable for continuous production scenarios (such as municipal sewage treatment plants).
B.High Dosing Convenience
Flocculant emulsion CPAM(JF1115) can be directly dosed after dilution (usually diluted to 0.1%-0.5%). There is no need to worry about dust pollution as in the case of powder (PAM powder dust may irritate the respiratory tract). The operating environment is more user-friendly, reducing the cost of labor protection.
C.Stable Flocculation Efficiency(JF1115).
The CPAM flocculant molecular chains in the emulsion are more evenly dispersed. After dissolution, the molecular chains of flocculant emulsion CPAM have good extensibility, which can have a larger contact area with the negatively charged colloids in the sewage (such as organic sludge and suspended solids in municipal sewage). The charge-neutralizing and bridging flocculation effects are more rapid. Especially in the sludge dewatering process, it can shorten the filtration time and reduce the moisture content of the filter cake.
D. Wide Applicability
It has better adaptability to the system pH than some powdered types (especially products with medium and low cationicity). Flocculant CPAM performs stably in acidic to neutral sewage and has good compatibility with inorganic flocculants (such as PAC, FeCl₃). They can be used in combination to improve the treatment efficiency.
3. Precautions for Use--Emulsion flocculant for water treatment (Compared with the Powdered Form) A. More Stringent Storage Conditions
The flocculant emulsion CPAM contains a certain amount of organic solvents (such as the oil-phase carrier). It needs to be stored in a sealed and light-proof place, with the temperature controlled between 5-30℃. Avoid low - temperature freezing or high - temperature demulsification (after freezing, the molecular chains break, and the efficacy decreases; high temperatures can easily lead to oil - water separation). The storage period is usually12 months (shorter than the over 2 - year storage period of the powdered form).
B. Precise Dilution Ratio Required
Due to its relatively low solid content, dilution needs to be calculated according to actual requirements (for example, to dilute a 50% solid - content emulsion to 0.1%, 499 times the amount of water needs to be added). The diluted emulsion of flocculant CPAM should be used up within 24 hours. Prolonged storage can lead to failure due to microbial growth or slow degradation of molecular chains.
C. Avoid Mixing with Strong Electrolytes
The molecular chains of CPAM flocculant in the emulsion are more sensitive to high-concentration salts (such as calcium and magnesium ions). If the salt content in the sewage is too high, it may cause the molecular chains to contract. Compatibility needs to be tested in advance. It is strictly prohibited to directly mix with anionic agents (which will cause charge neutralization and produce flocculation precipitation).
D. Balance of Cost and Dosage The cost per unit of active ingredient is usually higher than that of the powdered form (due to the complex emulsion preparation process). However, considering the low dissolution energy consumption and high dosing efficiency, in large-scale continuous operation scenarios (such as large-scale sewage treatment plants), the comprehensive cost may be more favorable.
Due to the special molecular structure(Cross linked polyacrylamide), JF1115 can easily capture solid like a net in dewatering or concentration process.
4. Summary of Applicable Scenarios
Cationic Polyacrylamide Emulsion--JF1115 is particularly suitable for scenarios with high requirements for treatment efficiency and operational convenience, such as: Sludge dewatering in municipal sewage treatment plants (plate-frame filtration, centrifugal dewatering); Rapid flocculation treatment of organic sewage from food processing, slaughterhouses, printing and dyeing industries, etc.; This type of emulsion polyacrylamide(JF1115) is used in machine of centrifuge, belt pressure filter and other dewatering machine in dewatering process. On-line dosing systems in continuous production lines (reducing equipment investment in the dissolution process).
Its core competitiveness lies in “rapid dissolution + high-efficiency flocculation + low-intensity operation”, but good management in storage and cost control is required to achieve the best results.
















