CPAM Emulsionr in Wastewater
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 2000Metric Tons per Month
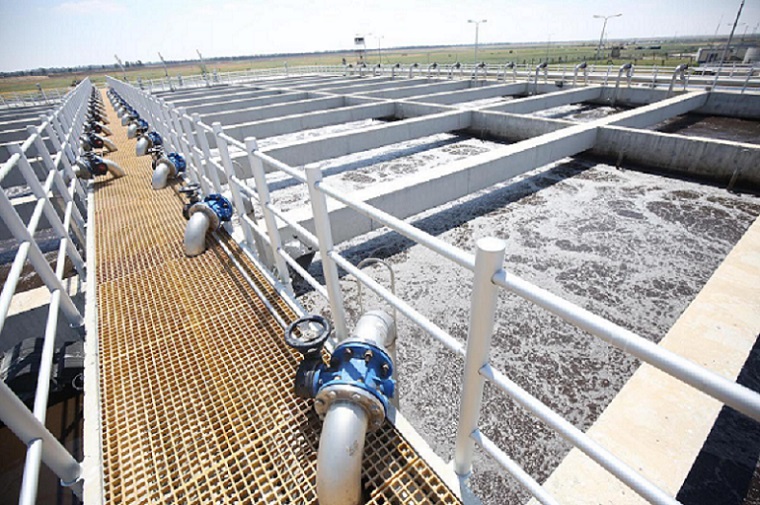
1. CPAM for wastewater is used for dewatering process in STP.
2. Wastewater chemicals liquid polyacrylamide is our company main product which is made by DAC or DMC copolymerized with
acrylamide.
3. The CPAM for wastewater(cationic polyelectrolyte emusion CPAM) produced by us is a link-crossed polymer product.
Download
The treatment mechanism of cross linked polymer cationic polyelectrolyte emulsion CPAM on sludge is based on the precise matching between the structural characteristics of CPAM for wastewater flocculant emulsion and the colloidal characteristics of sludge (negative charge, dispersion stability).
Through multiple synergistic effects, it realizes the agglomeration of sludge, improvement of dewatering performance, and solid liquid separation. The following is an analysis from the following aspects:
1. The Root Causes of "Difficult to treat" Sludge: Colloidal Stability and Structural Characteristics Sludge is a complex system composed of microbial cells, organic residues, inorganic particles, and bound water. The core difficulties are as follows:
1). Electrostatic Stability of Colloidal Particles: More than 90% of the suspended particles in sludge carry negative charges on their surfaces due to the adsorption of anions (such as phosphate and carboxylate). The particles are difficult to approach each other due to "like charge repulsion".
2). Hydration Film Barrier: The particles adsorb water molecules on their surfaces to form a hydration film, which further hinders particle agglomeration.
3). High Water holding Capacity: The large specific surface area and pore structure of fine particles firmly bind a large amount of water, making it difficult to dewater directly.
2. Core Action Mechanisms of Cross linked CPAM for wastewater flocculant Emulsion
1). Charge Neutralization and Double layer Compression: Breaking Colloidal Stability
The cationic groups (such as quaternary ammonium groups) on the cross linked CPAM for wastewater flocculant emulsion molecular chain neutralize the negative charges on the surface of sludge particles through electrostatic attraction, reducing the absolute value of the ζ - potential on the particle surface (from -30 to - 50 mV to - 10 to 0 mV), and significantly weakening the "charge repulsive force". Charge neutralization also compresses the double layer on the particle surface (the diffusion layer becomes thinner), reducing the distance between particles to the range dominated by Van der Waals forces (intermolecular attractive forces), creating conditions for subsequent agglomeration.
2). Adsorption Bridging: Constructing "Particle-Polymer-Particle" Aggregates
The cross linked structure makes the industrial wastewater CPAM chemicals molecular chain more stable (with strong shear resistance), and the amide groups (-CONH₂) on the molecular chain can adsorb sludge particles (including colloids, microorganisms, and organic matter) through hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The long chain molecules connect multiple dispersed particles simultaneously, forming a three dimensional floc nucleus of "particle - polymer - particle". As more particles are "bridged", the floc nucleus gradually grows into large flocs (with a particle size of up to several hundred microns).
Advantages of Cross linking of CPAM for wastewater flocculant emulsion: Compared with linear CPAM for wastewater flocculant emulsion, the cross linked molecular chain is less likely to break, has a stronger bridging ability, and the formed flocs are more compact and have better shear resistance.
3). Sweep Flocculation: Forcibly Enveloping Fine Particles and Bound Water
When the dosage of industrial wastewater CPAM chemicals reaches a certain concentration, its cross linked network molecular chain can, like a "fishing net", actively envelop fine particles (such as nanoscale colloids) that have not been charge neutralized or bridged, forcing them into the flocs.
The network structure also squeezes the interstitial water and some surface - bound water in the sludge, releasing the water from the inside of the flocs to the outside (free water), facilitating subsequent dewatering.
4). Synergistic Effect of Emulsion Form: Improving Reaction Efficiency - Emulsion - type CPAM (water in oil or water in water) has better dispersibility than dry powder. It can dissolve quickly and distribute evenly in the sludge, avoiding "incomplete particle encapsulation" or "over flocculation" (resulting in small flocs) caused by local high concentrations.
The tiny droplets in the emulsion (usually 1-10 μm) can quickly contact the sludge particles, shortening the reaction time of charge neutralization and adsorption bridging, and improving the treatment efficiency.
5). Strengthening Dewatering Performance: Improving Floc Structure and Water Release
The flocs formed by cross linked cationic polyeletrolyte emulsion CPAM have a dense structure (low porosity), which can reduce the "water holding space" inside the flocs. At the same time, the cationic groups bind to the negatively charged hydrophilic substances in the sludge, reducing their hydrophilicity and promoting water separation.
This structural optimization reduces the "moisture content of the filter cake" (for example, from 90% to 60% - 70%), improves the strength of the filter cake, and reduces the problem of "mud leakage" during filtration.
3. Synergistic Effects of the Mechanisms and the Final Goals
The above mechanisms do not act in isolation, but rather a synergistic process of charge neutralization first breaking stability → adsorption bridging connecting particles → sweep flocculation expanding flocs → emulsion form ensuring uniform reaction.
Ultimately, it achieves: The transformation of sludge particles from a dispersed state to an aggregated state (floc formation). The conversion of bound water to free water (improvement of dewatering performance).
The improvement of solid liquid separation efficiency (accelerated sedimentation speed and reduced filtration resistance), laying the foundation for subsequent sludge reduction (such as dewatering), stabilization (such as anaerobic digestion), or harmless treatment (such as incineration). In short, the cross linked cationic polyelectrolyte emulsion CPAM precisely solves the problems of colloidal stability and high water - holding capacity of sludge through multi level actions of "charge regulation - structural connection water release", and is an efficient "flocculation - dewatering" aid in sludge treatment.

Cationic polyelectrolyte emusion CPAM products(Flocculant emulsion) are used for dewatering process in industrial wastewater CPAM chemicals treatment.
Our technical team could supply customized technical service according to the paramters of flocculant emulsion,such as different sewage parameters and different sewage type.

Industry-specific attributes
| Name | Polyacrylamide Emulsion (Industrial wastewater CPAM chemicals) | |||
| Chemical Formula | (C3H5NO)n | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
| Appearance | Flocculant emulsion | |||
| Solid Content | 48% | |||
| Viscosity Range(ml/g) | 1200~1600 | |||
| Residue | 0.12% | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| Cationic Charge | 80% | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | 40 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















