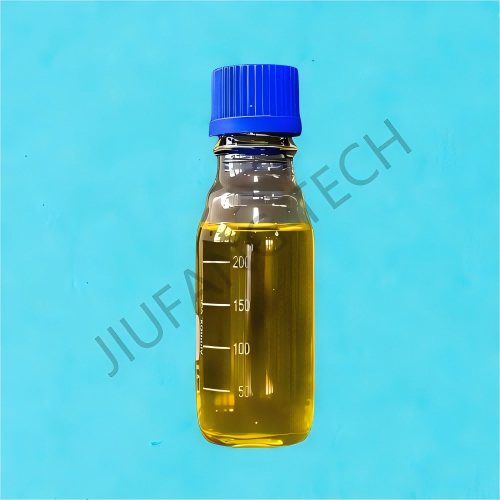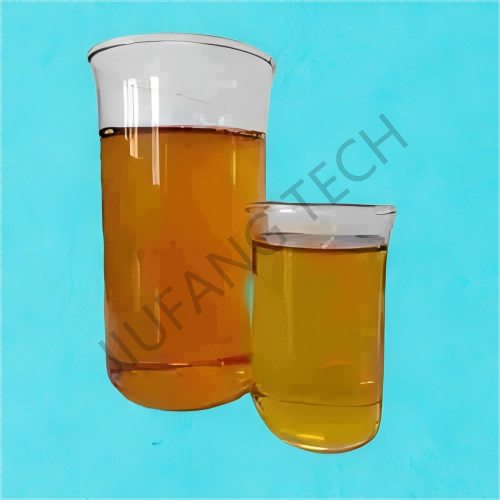
Polyamine Liquid For Sewage
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 1000Metric Tons per Month
1. Polyamine liquid used for the decolorization treatment of high-colority wastewater in dye factories.
2. Chemical polyamine solution can also be used in the treatment of industrial wastewater.
3. Sewage use Polyamine is suitable for 50% content polyamine product.
Download
Polyamine liquid is a class of polymers containing multiple amino groups (-NH₂) or imino groups (-NH-). Due to the positively charged groups on their molecular chains and the adjustable molecular structure, they are widely used in the treatment of oily wastewater and sewage use polyamine in oilfields.
The oily wastewater in oilfields has a complex composition, containing crude oil (emulsified oil, dispersed oil), suspended solids, salts (high salinity), additives (such as surfactants, polymers), etc., which makes it difficult to treat. Polyamine liquid, with their unique physical and chemical properties, play a crucial role in processes such as demulsification, flocculation, and purification.
1. Characteristics and Treatment Difficulties of Oily Wastewater in Oilfields
The core characteristics of oily wastewater in oilfields determine its treatment difficulty and also form the targeted background for the application of polyamine solution:
High Emulsification: The crude oil in the wastewater often forms a stable oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion with surfactants (such as sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate used for oil displacement). The oil droplets have a small particle size (usually < 10μm), strong interfacial charge, and are difficult to separate naturally.
High Salt and High Salinity: It contains a large amount of metal ions such as Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and Na⁺, and the salinity can reach 10⁴-10⁵ mg/L, which has a significant impact on the stability and effectiveness of common agents.
Complex Composition: It contains polymers (such as polyacrylamide used for oil displacement), resins, asphaltenes, etc., which further increase the viscosity and stability of the wastewater.
High Treatment Requirements: The wastewater needs to meet the reinjection (water for oilfield development) or discharge standards (such as oil content < 10 mg/L), and strict requirements are imposed on the treatment efficiency.
2. The Action Mechanism of Polyamine liquid in Oily Wastewater in Oilfields
The action of polyamine liquid is based on the characteristics of their molecular structure (cationic charge, long-chain structure), and the purification of wastewater is mainly achieved through the following mechanisms:
1). Charge Neutralization. The oil droplets and colloidal particles (such as clay, organic matter) in oilfield wastewater usually carry a negative charge due to the adsorption of anionic surfactants, with a relatively high zeta potential (usually > - 30 mV) and strong stability. The amino/imino groups on the polyamine liquid molecular chain become positively charged after protonation. They can be electrostatically attracted to the negatively charged oil droplets and colloids, neutralize their surface charges, and reduce the zeta potential (usually to <-15 mV), destroying the stability of the emulsion and causing the oil droplets and particles to lose their repulsive force and aggregate.
2). Bridging Flocculation Polyamine liquid have a relatively long molecular chain (with a molecular weight usually ranging from 10⁴ to 10⁶). Multiple active sites on the molecular chain can simultaneously adsorb multiple oil droplets or particles. Through the "bridging" effect, the dispersed fine particles are connected into larger flocs (with a particle size reaching several hundred microns), accelerating their sedimentation or floating.
3). Enhancing Demulsification Effect For stable emulsions, polyamine liquid can penetrate into the oil-water interface, replace the surfactant molecules on the interface, and destroy the strength of the interfacial film, causing the emulsified oil droplets to merge into large oil droplets and achieve oil-water separation.
3. Specific Application Scenarios of Polyamine liquid According to the treatment stages (pretreatment, advanced treatment) of oily wastewater in oilfields, the application methods and purposes of polyamine liquid is different:
1). Pretreatment Stage: Demulsification and Primary Oil Removal
Applicable Scenarios: For wastewater with a high oil content (usually 100-1000 mg/L), such as wastewater from oil production wellheads and wastewater after separation at the central gathering station.
Function: Through demulsification and flocculation, convert emulsified oil into free oil, make the oil droplets aggregate and float, and at the same time remove some suspended solids, reducing the load of subsequent treatment.
Application Method: Usually added alone or in combination with inorganic demulsifier (such as calcium chloride), with a dosage generally of 50-200 mg/L. After treatment, the oil content of the wastewater can be reduced to less than 50 mg/L.
2). Advanced Treatment Stage: Purification and Meeting Standards
Applicable Scenarios: The wastewater after pretreatment (with an oil content of 10-50 mg/L) needs to be further treated to meet the reinjection or discharge standards (oil content <10 mg/L).
Function: For the remaining tiny oil droplets and suspended solids, polyamine liquid strengthen flocculation to form larger flocs. Combined with precipitation or filtration processes (such as inclined - plate sedimentation, air flotation), the oil and suspended solids are deeply removed.
Application Method: Often combined with coagulant aids (such as polyaluminum chloride, PAC). The bridging effect of polyamines is used to strengthen the small flocs formed by PAC, improving the sedimentation efficiency. After treatment, the oil content of the wastewater can be reduced to less than 5 mg/L, and the suspended solid content is < 20 mg/L, meeting the reinjection (such as the reinjection requirement for low - permeability oilfields is an oil content < 5 mg/L) or discharge requirements.
3). Special Scenarios: Treatment of High - Salt/High - Temperature Wastewater Oilfield wastewater is often in a high-temperature (40-80℃) and high-salinity environment. Ordinary flocculants (such as aluminum salts, iron salts) are prone to hydrolysis and failure. However, the molecular chain of polyamine liquid has strong stability (salt - resistant, temperature - resistant). It can maintain the charge density under high-salt conditions and is not easy to decompose at high temperatures. Therefore, it is suitable for the treatment of wastewater in special scenarios such as Bohai Oilfield (high salinity) and heavy - oil oilfields (high temperature).
4. Advantages and Precautions of Polyamine liquid Application
Advantages
High Efficiency: Compared with traditional agents (such as PAM, aluminum sulfate), polyamine liquid has a higher charge density, faster demulsification and flocculation speeds, and the treated wastewater has a high clarity.
Strong Adaptability: Excellent salt-and temperature-resistant properties, which can adapt to the complex working conditions of oilfield wastewater.
Less Sludge: The formed flocs are compact and have good dewatering performance, reducing the cost of sludge treatment.
Good Compatibility: Can be used in combination with other agents (such as demulsifiers, bactericides) without affecting the overall treatment process.
Precautions
Dosage Control: Excessive addition will lead to the residual polyamine liquid in the water, increasing the COD or causing secondary pollution. The optimal dosage needs to be determined through small - scale tests (usually 50-300 mg/L).
Type Screening: The molecular weight and amino group content of polyamines affect the effect (for example, low-molecular-weight polyamine liquid have strong demulsification properties, and high - molecular - weight polyamine liquid have good flocculation properties). The appropriate type needs to be selected according to the properties of the wastewater (such as oil content, degree of emulsification).
Toxicity Impact: Some polyamine liquid (such as unmodified aliphatic polyamines) may inhibit the microorganisms in subsequent biochemical treatment. If the wastewater needs biochemical treatment, low-toxicity modified polyamine liquid (such as epichlorohydrin - amine copolymers) should be selected.
Industry-specific attributes
| Name | Polyamine liquid | |||
| Molecular Formula | C18H35N3O3 | |||
| Application | Water Treatment | |||
Other Attributes
| Appearance | Colorless to white viscous liquid | |||
| Odor | Odorless | |||
| Content | 50% | |||
Supply Ability
| Supply Ability | 1000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















