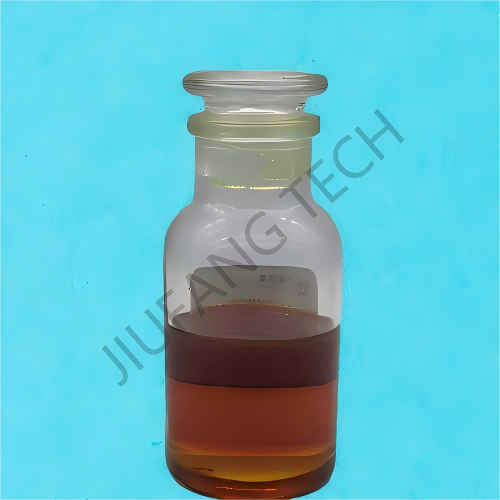
Demulsifier additive
Brand Shenyang Jiufang
Product origin China
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 10000MT/Year
Demulsifier additive compositions are mainly copolymers of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide.
Demulsifier dewatering means that it is dehydration process in crude oil treatment.
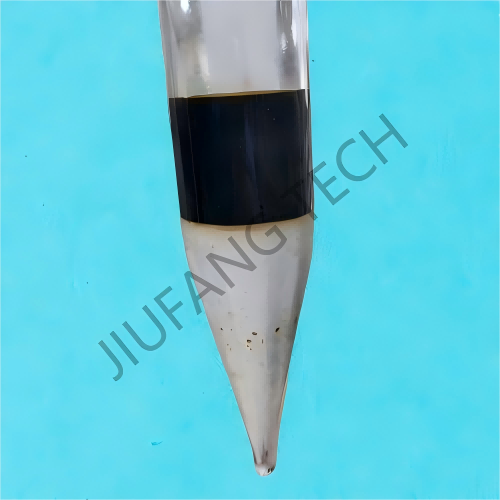
Demulsifier additive for crude oil can effectively destroy the stable structure in the crude oil emulsion, separating the emulsified water from the crude oil.
Download
At present, there are a wide variety of demulsifier additive for crude oil at home and abroad, but most of demulsifier additive compositions are non-ionic demulsifier additive and their demulsification effects vary.But in terms of their molecular composition, they are mainly copolymers of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide. Currently, there are mainly five types of commonly used non-ionic demulsifier additive in oilfields:
1.Peregal or OP type, which is a copolymer of high-carbon alcohol or alkylphenol as the initiator and ethylene oxide.
2.SP type, a copolymer with high-carbon alcohol as the initiator.
3.BE and BP types and their modified products, two or three segment copolymers of propylene glycol with ethylene oxide and propylene oxide and their modified products.
4.GP type, a three-segment copolymer with glycerol as the initiator.
5.AR and AF types and their modified products, binary and ternary copolymers with alkylphenol formaldehyde resin as the initiator and their modified products.
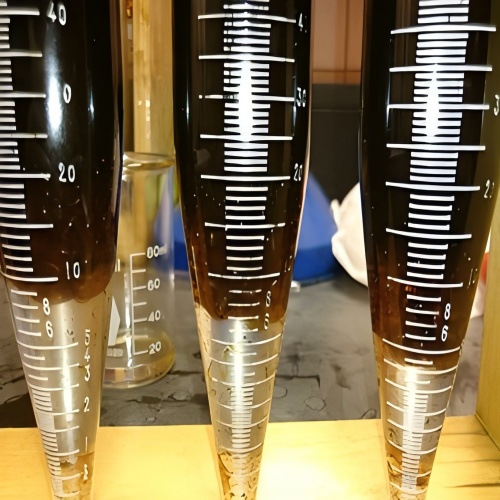
Demulsifier dewatering can effectively disrupt the stable structure in the crude oil emulsion, separating the emulsified water from the crude oil. This helps to reduce the water content of the crude oil and thereby enhance its purity. For instance, after demulsification treatment, the water content of the crude oil can be decreased from a relatively high percentage (such as 10%--30%) to a lower level (such as 0.5%--3%), making it more in line with the processing requirements of refineries.
The petroleum industry is the primary application field of demulsifier additive for crude oil.
The core objective is to separate the emulsions formed by crude oil and associated water (most crude oil is a "water-in-oil" emulsion, and some high-water-cut crude oil is an "oil-in-water" emulsion).
Crude Oil demulsifier dewatering: During the crude oil extraction process, due to the mixing of formation water, injected water and crude oil, a stable emulsion will be formed (the water content can reach 30%-80%). Demulsifier additive for crude oil (such as polyethers, polyamines) can dissolve in the aqueous phase, quickly diffuse to the oil-water interface, break the interfacial film formed by emulsifiers (such as asphaltenes, resins), promote the coalescence of water droplets into large droplets and sedimentation, ultimately achieving oil-water separation. These demulsifier dewatering is especially suitable for high-water-cut crude oil. Because of their stronger dispersibility in the aqueous phase, their demulsification efficiency is higher than that of oil-soluble demulsifiers (the dehydration rate can reach over 95%).
Treatment of Oily Wastewater in Refineries: The wastewater generated during the refining process (such as desalting wastewater, washing wastewater) contains a large amount of emulsified oil (oil-in-water emulsion). Water soluble demulsifier dewatering can make the oil droplets coalesce and float, facilitating the recovery of oil by subsequent oil separating tanks or flotation equipment. This reduces the oil content in the wastewater (from several hundred mg/L to less than 10mg/L), minimizing the impact on subsequent biochemical treatment.














