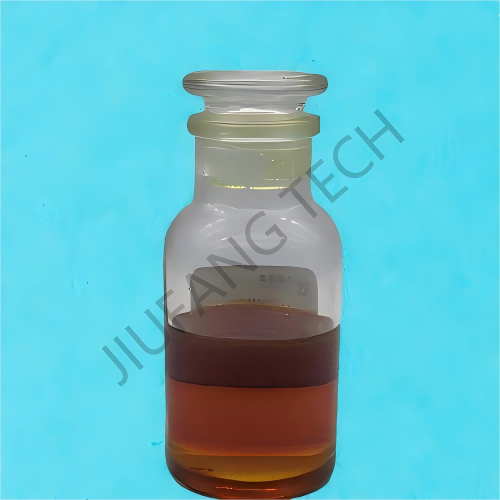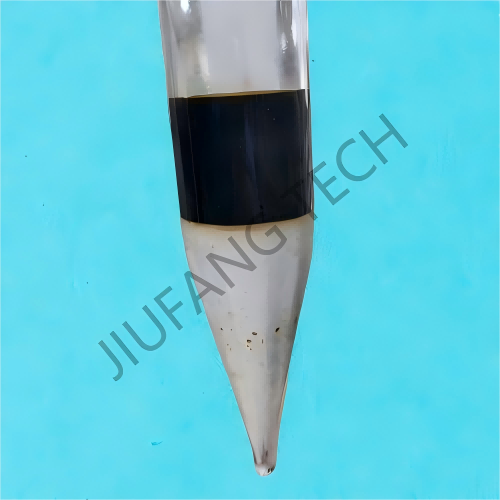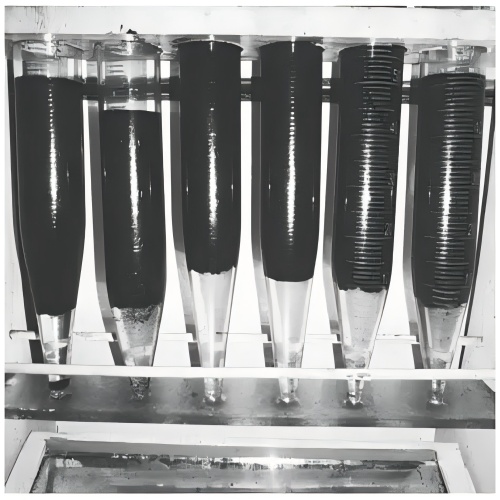
Demulsifier Dewatering in produced water
Brand Jiufang
Product origin Shenyang
Delivery time Lead time: 7days
Supply capacity 1000Metric Tons per Month
1. Demulsifier dewatering(demulsifier dehydration) is widely use for crude dehydration in oilfield.
2. Using demulsifier additive for crude oil (Dewatering in produced water) is a product formed for dewatering in produced water
by the block polyether of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide
Download
Demulsifier additive for crude oil is one of the core chemical agents in the treatment of produced fluids in oil and gas extraction.
Their key function is to disrupt the stable oil-water emulsions in the produced fluids, enabling efficient separation of oil and water, and laying the foundation for subsequent crude oil gathering and transportation, refining, and compliant treatment of sewage.
The following explanation is presented from the aspects of application background, mechanism of action, specific scenarios, and key points:
1. Application Background of demulsifier dewatering in produced water: Formation and Hazards of Emulsions in Produced Fluids During oil and gas extraction, crude oil mixes with formation water and injected water (such as water injection and polymer solutions in secondary/tertiary oil recovery) under the effects of high pressure, shearing, and stirring. Meanwhile, natural emulsifiers in the formation (such as asphaltenes, resins, paraffin, clay particles, etc.) adsorb at the oil-water interface, forming stable emulsions (commonly water-in-oil (W/O) or oil-in-water (O/W), or complex emulsions).
These stable emulsions can cause the following problems: An increase in the water content of crude oil, which raises transportation energy consumption (the presence of water increases viscosity and density). In subsequent refining, water can lead to equipment corrosion and catalyst poisoning. If the oily sewage is directly discharged, it will pollute the environment and result in waste of oil resources. The high stability of the emulsion can block pipelines and equipment, affecting the extraction efficiency.
2. Mechanism of Action of Demulsifier additive for crude oil.
Demulsifier additive for crude oil disrupt the stability of emulsions and promote oil-water separation through the following methods:
1). Competitive Adsorption at the Interface: Demulsifier additive for crude oil agents molecules (such as polyethers and amines) are more likely to adsorb at the oil-water interface than natural emulsifiers, replacing the original emulsifiers and weakening the strength of the interfacial film.
2). Reduction of Interfacial Tension: The hydrophilic-lipophilic groups of demulsifier additive for crude oil agent molecules (with an appropriate HLB value) can reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water, making it easier for small droplets to collide and coalesce.
3). Destruction of the Interfacial Film Structure: Some demulsifier additive compositions (such as cationic types) can neutralize the charge of natural emulsifiers (which are negatively charged), destroying the electrical stability of the interfacial film. Or through molecular chain entanglement, the brittleness of the interfacial film increases, making it prone to rupture.
4). Promotion of Droplet Coalescence: Dewatering in produced water agent can connect multiple small droplets through a "bridging" effect, promoting their aggregation into large droplets, which eventually settle and separate due to the density difference.
3. Specific Application Scenarios
The application of dewatering in produced water agent spans the entire process of produced fluid treatment. The key scenarios include:
1). Wellhead and Gathering and Transportation Links-After the produced fluid is discharged from the wellhead, it first undergoes preliminary separation (such as in a free - water knockout). Adding a demulsifier emulsion dewatering agent at this time can quickly remove free water, reducing the water content of crude oil (from over 50% to less than 10%) and decreasing the subsequent treatment load. For high-viscosity and high-wax-content crude oil, demulsifier additive for crude oil agents are often used in combination with viscosity reducers and paraffin inhibitors to improve the gathering and transportation efficiency.
2). Crude Oil Dewatering Process
Thermochemical Dewatering: Add a dewatering in produced water agent under heating conditions (40-80°C, reducing viscosity), and most of the water is separated through static sedimentation. This is suitable for medium to low stability emulsions.
Electrochemical Dewatering: For high stability emulsions (such as W/O type with a high content of emulsifiers), under the action of an electric field (water droplets move directionally with charge), combined with a demulsifier to promote the collision and coalescence of water droplets, ultimately reducing the water content of crude oil to less than 0.5% (meeting the export standard).
3).Treatment of Oily Sewage
The sewage generated after the dewatering of produced fluids has a high oil content (1000-10000 mg/L) and needs further treatment (to meet the standards for reinjection or discharge). For the O/W type emulsion in the sewage, water soluble demulsifier additive for crude oil need to be added to disrupt the interfacial film of oil droplets, causing the oil droplets to coalesce and float. Then, through processes such as flotation and filtration, the oil content is reduced to less than10 mg/L.
4). Treatment of Special Produced Fluids
Tertiary Oil Recovery Produced Fluids: Such as polymer-flooding (containing PAM) and ASP flooding (containing alkali, surfactant, and polymer) produced fluids. The emulsions have extremely high stability. Special salt-resistant and alkali-resistant dewatering in produced water agents(such as modified polyetheramines and block copolymers) are required, and demulsification is achieved through a molecular structure resistant to harsh environments.
Heavy Oil/Extra-Heavy Oil Produced Fluids: Due to the high content of asphaltenes and resins, the emulsions have high viscosity. Dewatering in produced water agents with a high HLB value (such as polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene block copolymers) are needed, combined with high temperatures (100-200°C) to enhance demulsification.
4. Selection and Application Points of demulsifier additive for crude oil
1).Compatibility: The type of demulsifier dewatering agent needs to be selected according to the type of emulsion (W/O or O/W), the properties of crude oil (density, viscosity, composition of emulsifiers), and the water quality (mineralization degree, pH). Non-ionic demulsifiers are the most widely used (such as polyethers); cationic demulsifiers are suitable for systems with a high clay content.
2. Dosage Control: The dosage is usually 50-500 mg/L (based on the produced fluid). Excessive dosage may cause secondary emulsification, and the optimal dosage needs to be determined through bottle tests.
3. Process Coordination: The demulsification effect is closely related to temperature, residence time, and stirring intensity (for example, high temperature accelerates demulsification but increases energy consumption, and a balance needs to be struck).
4. Environmental Requirements: Preference should be given to biodegradable and low-toxicity demulsifier dewatering agent(such as modified natural polymer products) to avoid polluting the soil or groundwater.
5. Development Trends With the advancement of oil and gas extraction towards deep wells, heavy oils, and tertiary oil recovery fields, demulsifier emulsion dewatering is developing towards :
high - efficiency(low dosage, rapid demulsification), multi - functionality (combining demulsification, viscosity reduction, and scale prevention), environment - friendliness(biodegradable), and intelligence (custom-designing the molecular structure for specific produced fluids) to meet the treatment requirements of complex produced fluids.
In summary, demulsifier dewatering agent is crucial for achieving crude oil purification and compliant sewage treatment by precisely disrupting the stability of emulsions in produced fluids, directly influencing the economic and environmental performance of oil and gas extraction.

Industry-specific attributes
| Name | Demulsifier additive for crude oil | |||
| Items | Indicator | |||
| Application | Demulsifier dewatering | |||
Other Attributes
| Appearance | Yellow to Brown liquid,no impurities | |||
| Odor | Slightly Odorless | |||
| Density (20°C ) | 1.1- 1.25 g/ml (9.51-9.85 lb/gal) | |||
| Content(%) | >35 | |||
| Viscosity (20°C ) | < 150cp | |||
| PH (20°C) | 3~6 | |||
| Freezing point | 12°C (10°F) | |||
| Boiling point | 99 °C (210°F) | |||
| Solubility in water | Soluble,easily dispersible | |||
| Closed flash point,℃ | ≥93.3 | |||
| Shelf life | 12 months | |||
Supply Ability
| Supply Ability | 1000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |